TRANSFORMER
Transformer :-
A transformer is a stationary electrical device. Which is transfer the electrical energy one coil wire to two or more coil wire. Its base on a electromagnetic induction. that can reduce or decrease the alternating voltage without loss of energy, it reduces the voltage of the alternating current, hence this voltage is called the alternating voltage, decreasing the voltage of the transformer current without changing it.Transformer was invented by Michael faraday and Joseph Henry showed it to the world in 1831. Transformers in Hindi are called transformers.
Its simple use is as the transformer reduces the voltage such that a device operates on a 12 volt direct current, then the transformer reduces the alternating current coming in our house to 220 volt to 12 volt. This is 12 volt of alternating current Let's use rectifier to convert it to dc
Transformer Symbol
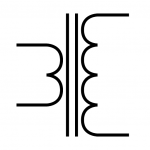 |
| Transformer Symbol |
Core of transformer
The core in the transformer is in the middle. It is made of laminated steel plates which are of strip type. There is a minimum Air Gap between all these leaves. It reduces the currents. Winding is wrapped around the core.
 |
| TRANSFORMER |
Winding
Winding The wires that are rotated are called winding. single transformers have two winding, one is primary winding and the other is one secondary winding and if the transformer is three phase then it has three primary winding and three secondary winding all from the insulated layer. Stays in contact with each other
Transformer EMF Equation
In a transformer, source of alternating current is applied to the primary winding. The current in the primary winding (called as magnetizing current) produces alternating flux in the core of transformer. This alternating flux gets linked with the secondary winding by core, because of the phenomenon of mutual induction an emf gets induced in the secondary winding. Magnitude of this induced emf. which is called EMF Equation. |
| Transformer EMF Equation |
Types of Transformer base on construction
1:- Core Type Transformer
2:- Shell Type Transformer
1 CORE TYPE TRANSFORMER
In core type transformer is closed core (core form). The primary and secondary winding are wound outside the surround the core. |
| CORE TYPE TRANSFORMER |
2 SHELL TYPE TRANSFORMER
In shell type transformer is shell core ( shell form). The primary and secondary winding are pass inside the core. which form as shell around the winding as shown in figure below.
 |
| SHELL TYPE TRANSFORMER |
Types of transformer base on Voltage level
1:- Step up Transformer
2:- Step down Transformer
1 Step up Transformer
The transformers which are used to increase the transformer voltage are called step up transformers. in this, the primary winding has less wire turn (Np) and in the secondary winding (Ns) the wire turns are high, in the first winding the wire turns can be seen. The number is less and the thickness of the wire is more. and in the second winding the wire is thinner and the number of turns is more.
2 Step down Transformer
The transformers which are used to decrease the transformer voltage are called step down transformers. in this, the primary winding has high wire turn (Np) and in the secondary winding (Ns) the wire turns are less, in the primary winding the wire turns can be seen. The number is high and the thickness of the wire is thinner. and in the second winding the wire is thick and the number of turns is less.
Power losses in transformer
The loss of energy in the transformer is the first copper loss. The coils used in the transformer are copper. It is heated due to current flow. Second is core loss.
Thank you for visit our website. very soon updateing....






5 Comments
Heloo
ReplyDeleteIts goood post
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteHi
ReplyDeleteBbbbhrex fgh
ReplyDelete